Hot filling is increasingly favored by juice manufacturers serving export markets, where food safety, shelf life, and operational efficiency must be carefully balanced. For decision-makers in the bottled beverage industry, choosing the right filling method directly affects product quality, cost effectiveness, and long-term reliability.
Among available options, hot filling remains one of the most widely adopted processes in juice manufacturing. This guide explains why global buyers prefer hot-fill PET juice manufacturers and how filling technology shapes export readiness and long-term brand risk!
What is Hot filling?
Hot filling is a proven beverage processing method used primarily for high-acid products (pH below 4.6) that require shelf stability at ambient temperatures. In this process, manufacturers fill the product into finished containers while it is still hot, seal the containers immediately, and then cool them in a controlled manner.
Typically, juice manufacturers heat the product to 85–95°C (185–203°F) to achieve microbial reduction before filling it directly into pre-sterilized PET bottles. This combination of thermal treatment and immediate sealing allows the heat to sterilize both the liquid and the internal surfaces of the bottle and closure.
For export-oriented drink brands, hot fill offers a reliable, integrated approach to food safety and shelf stability—well aligned with the expectations of global buyers and modern retail systems.
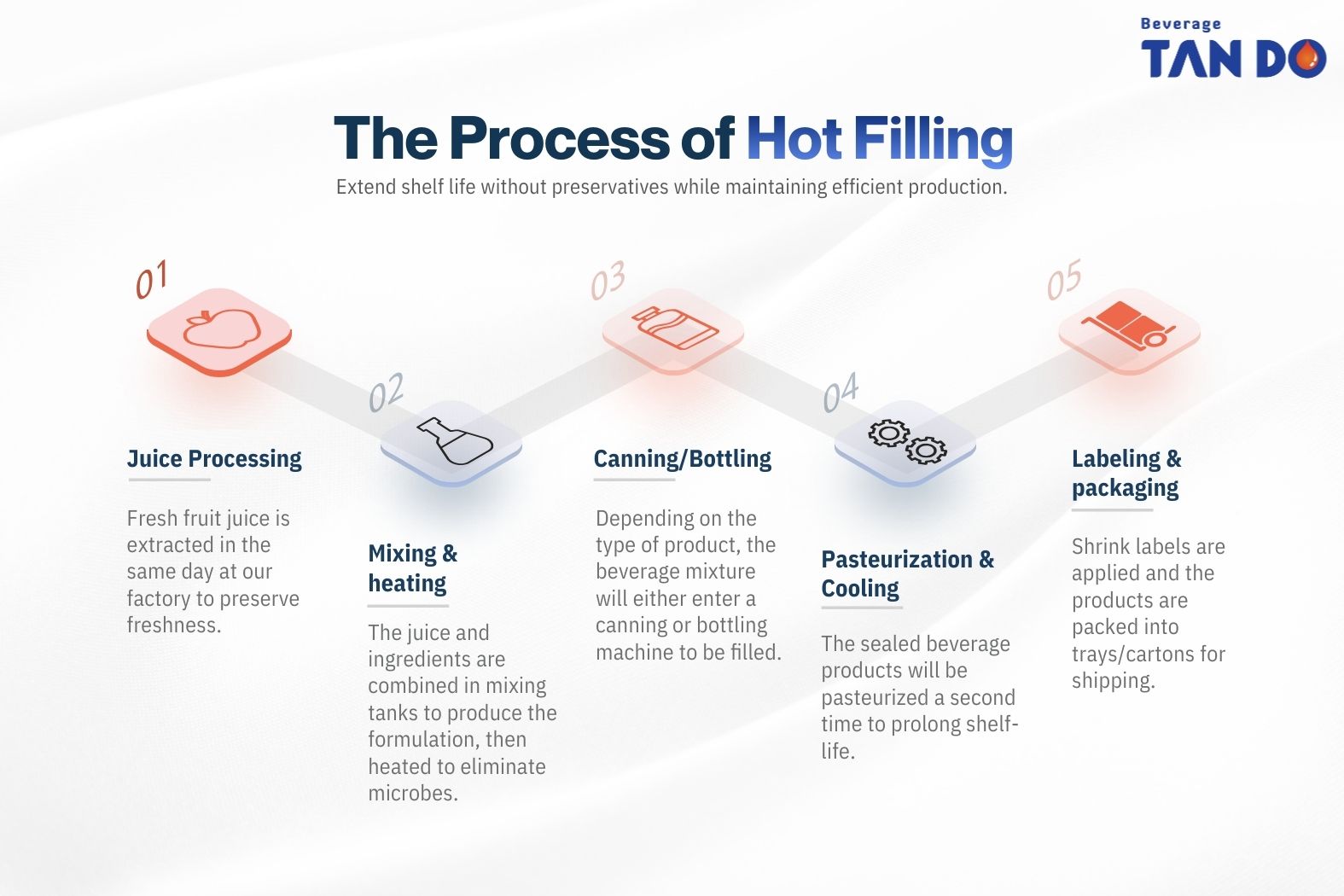
The Process of Hot Filling
Hot filling follows a controlled sequence of steps that allows juice manufacturers to extend shelf life without preservatives while maintaining efficient production.
1. Mixing & Heating
The juice and ingredients are combined in mixing tanks to produce the formulation, then heated in 90–95°C (190–203°F) in a heat exchanger for 15–30 seconds to eliminate microbes.
2. Canning/Bottling
Depending on the type of product, the beverage mixture will either enter a canning or bottling machine to be filled.
3. Pasteurization & Cooling
Then, manufacturer cool the product slightly to around 82–85°C (180–185°F) and fill it into containers at the filling station. In some cases, operators inject nitrogen into the headspace to remove oxygen and minimize oxidation.
Manufacturers then apply the closure immediately, allowing the heat to sterilize the inner surfaces of both the bottle and the cap. After sealing, operators tilt or invert the containers so the hot liquid contacts the closure, ensuring complete sterilization.
4. Labeling & Packaging
Finally, the sealed packages are rapidly cooled using water baths or spray systems. This step helps preserve flavor and nutritional quality while creating a vacuum inside the container, which inhibits microbial growth. Once cooled, the bottles are dried and labeled for distribution.

Why Juice Manufacturers Choose Hot-Fill PET Bottles for Export Markets
1. Shelf Life Built for Export Realities
Shelf life remains one of the most critical factors in export success. Juice products often spend extended periods in transportation, customs clearance, warehousing, and retail distribution before reaching consumers.
Hot-fill processing typically delivers 6–12 months of shelf life for suitable juice formulations without requiring refrigeration. While aseptic systems may extend shelf life further, hot-fill strikes a balance that many global buyers find commercially optimal:
- Sufficient shelf stability for export logistics
- Lower operational complexity
- Reduced dependency on ultra-sterile environments
For brand owners, this means fewer losses due to expiration, greater flexibility in inventory planning, and lower overall supply-chain risk.


2. Integrated Risk Control Through Process and Packaging
From a buyer’s perspective, the value of hot filling lies less in the technology itself and more in how effectively it manages food safety risk across the supply chain.
Hot-fill systems rely on preventive food safety principles:
- High-temperature treatment reduces microbial load at a critical control point
- Closed-loop filling and sealing limit recontamination
- Simpler system architecture reduces failure points
These benefits extend beyond the filling process to packaging design. Not all PET bottles can withstand hot-fill conditions. Export-focused juice manufacturers therefore rely on heat-set PET bottles, engineered to tolerate filling temperatures of up to 190–192°F (88–89°C) while maintaining shape, seal integrity, and clarity.


During hot-fill PET blow molding, manufacturers apply controlled heat to induce partial crystallization in the PET’s molecular structure. This controlled crystallization prevents bottle deformation when hot liquid is filled, ensuring consistent performance throughout long export journeys.
Together, process control and packaging integrity make hot fill especially attractive to global buyers who prioritize recall prevention, traceability, and audit transparency.
3. Operational Practicality at Export Scale
Although hot filling requires energy for heating and cooling, modern hot-fill lines have significantly improved efficiency through optimized heat recovery and cooling systems.
Compared with other filling methods, hot-fill PET lines typically offer:
- Lower upfront equipment investment
- Easier operation and maintenance
- Less dependence on highly specialized technical teams
For export-focused juice manufacturers, this operational simplicity translates into more stable production and predictable costs—factors that brand owners increasingly consider when selecting long-term manufacturing partners.


4. Strong Compatibility with Juice Formulations
While hot filling does not suit every beverage category, juice products are among the most compatible—particularly those with higher acidity, moderate to high sugar content, and smooth or semi-smooth textures.
Thermal processing helps deactivate spoilage enzymes while maintaining product safety and sensory quality. However, formulations containing heat-sensitive flavors or large particulates require careful optimization.
Experienced juice manufacturers understand these formulation nuances and design products specifically for hot-fill performance—another reason global buyers prefer partners with proven hot-fill PET capabilities.


Hot-Fill vs. Alternative Filling Technologies
When evaluating export manufacturing partners, global buyers often compare hot filling with aseptic and cold-fill technologies. Each method has its place, but hot-fill PET offers a distinct middle ground.
Compared with aseptic filling, hot fill:
- Requires lower capital investment
- Involves simpler validation and maintenance
- Reduces dependency on highly sterile environments
- Shortens commissioning and operator training timelines
Compared with cold filling, hot fill:
- Delivers significantly longer shelf life
- Reduces reliance on preservatives
- Provides stronger protection against microbial risk during distribution
For many export markets—particularly those with long transit times, variable infrastructure, or complex regulatory inspections—hot-fill PET offers a practical and commercially resilient solution.
Regulatory Acceptance in Global Export Markets
Another key reason buyers favor hot-fill PET manufacturers is the broad regulatory acceptance of the process across international markets.
Hot filling is well understood and widely recognized by food safety authorities in:
- North America
- Europe
- Japan
- Australia
- Southeast Asia and the Middle East
Because hot-fill processes are built around clearly defined critical control points (CCPs)—temperature, holding time, sealing integrity—they integrate smoothly into HACCP, BRCGS, FSSC 22000, and FDA-aligned food safety systems.
For brand owners, this regulatory familiarity reduces approval timelines, minimizes documentation friction, and lowers the risk of shipment delays or compliance disputes at destination ports.
Sustainability Considerations in Hot-Fill PET
Sustainability is increasingly part of export buyer evaluation, particularly for private label and multinational brands.
Hot-fill PET supports sustainability goals by:
- Using lightweight, recyclable materials
- Reducing product waste through extended shelf life
- Lowering logistics emissions compared with glass
- Supporting integration of rPET in compliant markets
While hot filling consumes energy, advances in heat recovery and line efficiency continue to narrow the environmental gap between hot-fill and alternative systems—making it a viable option for brands balancing sustainability with operational practicality.


Sum Up
Hot filling PET bottles continues to stand out as a preferred solution for export-oriented juice manufacturers, offering a balanced combination of shelf life, food safety assurance, operational practicality, and broad regulatory acceptance.
For global buyers, partnering with juice manufacturers equipped with proven hot-fill PET capabilities reduces supply-chain risk, accelerates market access, and supports consistent product quality as brands scale across international markets.
You may also like:
A definitive guide on hot-fill process in the beverage industry








